
China takes the lead in approving RCEP, the petrochemical industry structure will change
Release time: 2021-03-30 Click on the quantity:2361
On March 22, the head of the International Department of the Ministry of Commerce stated that China has now completed the approval of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement, which is the RCEP Agreement, and has become the first country to ratify the agreement. In addition, Thailand has also ratified the agreement. All the member states of RCEP stated that they will ratify the agreement before the end of this year and promote the agreement to enter into force on January 1 next year.

The Regional Com-prehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), initiated by the ten ASEAN countries, invites China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand to participate ("10+5"), through the reduction of tariffs and non-tariff barriers , To establish a free trade agreement for a unified market in 15 countries. Simply put, RCEP is a super free trade zone leading the world in various indicators. The 15 member states have a total population of 2.27 billion, a GDP of 26 trillion US dollars, and a total export value of 5.2 trillion US dollars, each accounting for about 30% of the global total.
On November 15, 2020, the "Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement" (RCEP), which has been negotiated for many years, was officially signed. The agreement will cover nearly half of the world’s population and nearly one-third of the world’s trade volume. The members include 10 ASEAN countries, China, There are 15 parties in Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand.
At present, RCEP is the world's largest free trade zone, covering about 30% of the world's population, 30% of the total economy and 30% of foreign trade. It has broad development prospects and huge potential. All members are full of expectations for RCEP.
In the later period, as the RCEP member states gradually approve the agreement, the world petrochemical industry structure will also change.
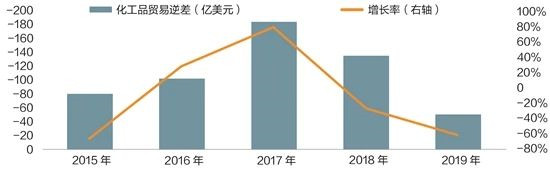
China's chemical product trade deficit and growth changes from 2015 to 2019
The status quo of trade between China and RCEP member countries
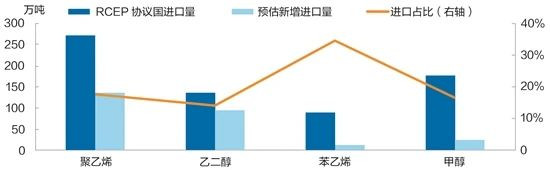
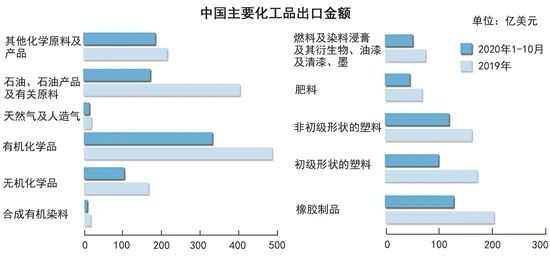
China's main chemical products imported from RCEP member countries and their import volume from January to October 2020
According to the official interpretation of the RCEP by the International Department of the Ministry of Commerce, more than 90% of the goods trade in the region will eventually achieve zero tariffs after the agreement comes into force. The final zero tariff rates promised by China to the ten ASEAN countries, Australia, and New Zealand are all about 90%. Except for the three least developed countries of Laos, Cambodia and Myanmar, the corresponding proportions of other ASEAN members, Australia and New Zealand pledged to my country are slightly higher than those of our country. my country’s final zero-tariff tax items promised to Japan and South Korea are both 86%, while Japan and South Korea’s promises to my country are 88% and 86% respectively.
The ten ASEAN countries refer to Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia. In 2020, the ten ASEAN countries will be my country's largest trading partners.
According to the trade information provided by ASEAN, chemical products have become important trade products between China and major ASEAN countries. my country and ASEAN are highly complementary in the chemical industry. The products my country imports from ASEAN are mainly primary raw material chemical products, such as primary form plastics, natural rubber and other chemical products. The chemical products imported by ASEAN countries from my country are mainly fertilizers, plastics and rubber products, pesticides, ethanol, phosphoric acid and so on.
South Korea is a strong export-oriented petrochemical industry with highly developed oil refining and chemical industries. Its export products account for a relatively high proportion of the industry’s total production. It is one of the largest exporters of petroleum products in Asia. Its petrochemical industry is mainly dominated by large domestic Korean conglomerates and has strong competitiveness. For naphtha, light cycle oil, etc., China mainly imports, and the main source country is South Korea.
Japan and China are highly complementary in the import and export of chemical products. China’s imports of chemical products from Japan are mainly high-end refining and chemical products, of which high-performance chemical products such as carbon fiber have the largest increase, while the largest proportion of Japanese chemical products imported from China are basic chemical products such as plastics. It is stronger than China in terms of high-end refining and fine chemicals capabilities.
China's petrochemical industry-related products imported from Australia are textiles and raw materials, and Australia's main chemical products imported from China are plastic and rubber products, which accounted for about 5% of its total imports in 2019.
New Zealand mainly imports textiles and raw materials, furniture, toys, and miscellaneous products from China. Plastics and rubber also occupy a certain proportion.
RCEP's impact on the petrochemical industry
Some scholars have predicted the cumulative impact percentage of RCEP on specific industries in China during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period based on the Global Trade Analysis Model (GTAP) and related data research.
Among them, the domestic output of the petrochemical industry (mainly including coking products, petroleum, refined oil, etc., basic chemicals, other chemicals, rubber and plastic products) will be suppressed, with an impact ratio of -0.11%. At the same time, product imports and exports are expected to be Received 2.92% and 1.75% respectively.
According to the above data, although RCEP has a positive impact on the import and export of products in the petrochemical industry, it still promotes imports more strongly. At the same time, domestic output will be suppressed to a certain extent in the next few years.
This is mainly because the current domestic production capacity is mainly low-end and medium-end products, and the products are highly substitutable. Faced with the gradually rising petrochemical industry in the ASEAN countries in the next few years, it will be affected to a certain extent; on the other hand, the production technology of high-tech additional products Domestic companies still lack production capacity, and the main impact of RCEP on the current trade situation comes from Japan and South Korea, and Japan and South Korea are known for exporting high-tech petrochemical products. Therefore, in the next few years, the domestic petrochemical industry will face a more intense competitive environment.
Forecast of the overall impact of RCEP on China's petrochemical industry after its entry into force
Yu Biying|Professor and PhD supervisor of the Energy and Environmental Policy Research Center of Beijing Institute of Technology
The reduction of tariffs on my country’s chemicals by member states is conducive to resolving excess capacity. my country has overcapacity in products such as synthetic ammonia, calcium carbide, polyvinyl chloride and fertilizers. After the agreement comes into effect, Japan will exempt trade tariffs on my country’s synthetic ammonia and urea, and tariffs on calcium carbide trade will also be directly reduced from the benchmark rate of 2.5% to zero; South Korea’s trade taxes on polyvinyl chloride, calcium carbide and synthetic ammonia will be separately The benchmark tax rates of 6.5%, 5.5%, and 1% are directly reduced to zero, and for fertilizers, the benchmark tax rate of 2% will be gradually reduced to zero within 15 years after its entry into force. The direct abolition and gradual reduction of tariffs will benefit the export of these chemicals, thereby helping to resolve excess capacity.
my country’s tariff reduction on chemicals from other member states may force industrial upgrading. On the one hand, it can reduce production costs for related downstream industries, and on the other hand, it will bring competitive pressure on chemical manufacturers, but in the long run, it may force industrial upgrading. For some chemicals that are highly dependent on foreign countries, my country has adopted a relatively conservative tariff policy. For example, for olefins, my country only reduced taxes to zero for Japan and South Korea in the 21st and 10th years of the agreement’s entry into force; for polyethylene, p-xylene (PX), purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and ethylene glycol my country has not made any commitments to reduce or cancel tariffs for major trading countries such as Japan and South Korea. For Australia, it has adopted a longer tax reduction period or slightly reduced the tax rate and will remain unchanged. To a certain extent, slow the rapid increase in external dependence.
Wu Zhiqiao|Longzhong Investment Research Polyolefin Market Researcher
At present, many high-end fine chemicals and new chemical materials in China still rely on imported resources, and Japan and South Korea are the main import sources of my country's high-end chemical materials. The signing of RCEP will help domestic downstream enterprises to reduce procurement costs.
In terms of polyethylene, there is currently a large gap in my country. Even if the new equipment is successfully put into production, it will still need to be imported in the short term. In 2021, South Korea, Malaysia and the Philippines will add 3.15 million tons of new polyethylene plant capacity, accounting for 24.4% of the total newly invested capacity. After the agreement comes into effect, it is expected that 65% of South Korea’s goods will implement a zero-tariff policy, which will stimulate its export trade to the greatest extent. Coupled with its advantageous geographical location, China’s imports of polyethylene products from South Korea are expected to increase, with an estimated increase of about 780,000 tons. . Malaysia and the Philippines will add more polyethylene capacity in the future. After the agreement takes effect, they will also stimulate their exports to China while meeting their domestic needs. The new increases are expected to be 530,000 tons and 48,000 tons, respectively.
In terms of ethylene glycol, from January to October 2020, my country’s main sources of imports from RCEP were Singapore, Japan, and South Korea. The import volume was 1.326 million tons, accounting for 14.1%. After the tariffs are lowered, imports from member countries are expected to increase further, especially those from Singapore, South Korea and Japan are more likely to increase. Taking into account the new production capacity of Japan and South Korea, it is estimated that the new increase will be 930,000 tons about.
In terms of styrene, from January to October 2020, my country’s imports of styrene in RCEP mainly came from Singapore, Indonesia, Japan and South Korea, with an import volume of 870,000 tons, accounting for 34.7%. It is expected that after the agreement comes into effect, the above-mentioned countries will also increase their exports to China while meeting their domestic needs, and the new increase is expected to be around 80,000 to 100,000 tons. In the future, my country will invest more styrene capacity (expected to add 7.65 million tons in 2020-2021). Japan and Singapore have already exported most of their sources to China, and there are no new production equipment. Therefore, the import volume of this part will be expected in the future. Gradually replaced by domestic production.
Source: MOLBASE

The "Plastic Recycling and Energy Chemical Carbon Neutrality Forum 2021" sponsored by ASIACHEM will be held in Huizhou on March 25-26, focusing on relevant policies, technologies, and markets.
Theme
Plastic pollution control and carbon neutrality "14th Five-Year" policy trend
Plastic production and the challenge of carbon peak and carbon neutral goals
Plastic recycling in Japan, the European Union, and the U.S.
Domestic and international advanced plastic recycling technology and industrial application
Analysis of the development prospects of recycled plastics and degradable plastics
PET recycling technology and downstream enterprise application situation
PP/PE/PC recycling technology and application prospects
Waste recycling, recycling cost and economic analysis
Evaluation criteria and application scenarios of recycled materials
Circular economy park development ideas and commercial demonstration
The status quo and trend of recyclable design ideas
Industry tour (to be confirmed)
Copyright: Zhejiang Everstand Mechanical Engineering Co.,Ltd Tel:+86-574-86111527 E-mail:nbcy2006@163.com Power by mdcm